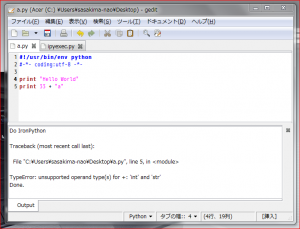
Gedit Windows 版から IronPython を起動する。
Python コードを開いて F5 キーを叩くと実行結果をボトムパネルに表示。
Gedit で Python スクリプトを debug – L’Isola di Niente
つまりコレを再現したい。
Gedit の Windows 版で External Tools が使えないのでソースコードを見る。
ちなみに External Tools も Python 製である。
8.11 fcntl — fcntl() および ioctl() システムコール
を使っていた、なるほどこれでは Windows では使えないわけだ。
前回は少し勘違いをしていたようで環境変数は External Tools が登録するようだ。
何にせよ Linux と Windows でまったく同じコードというのは不可能だよね。
とりあえず Python なんだから subprocess でなんとかならないか。
window オブジェクトからロケーションは得られるのだから強引にでも。
と思ってこんなプラグインを作ってみた。
ipyexec.gedit-plugin
[Gedit Plugin] Loader=python Module=ipyexec IAge=2 Name=Iron Python Execute Description=Iron Python Execute Authors=sasakima-nao <sasakimanao@gmail.com> Copyright=Copyright © 2013 sasakima-nao <sasakimanao@gmail.com> Website=http://palepoli.skr.jp/
ipyexec.py
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import gedit
import gtk
import os
import subprocess
IPYPATH = "C:\Program Files (x86)\IronPython 2.7\ipyw64.exe"
ui_str = """<ui>
<menubar name="MenuBar">
<menu name="ToolsMenu" action="Tools">
<menuitem name="ipyexec" action="ipyexec"/>
</menu>
</menubar>
</ui>
"""
class IpyExecPlugin(gedit.Plugin):
def __init__(self):
gedit.Plugin.__init__(self)
def activate(self, window):
self._window = window
manager = self._window.get_ui_manager()
self._action_group = gtk.ActionGroup("IpyExecActions")
# GtkActionEntry
# name, stock_id, label, accelerator, tooltip, callback
actions = [("ipyexec", None, "ipyexec", "F5", "ipyexec", self.on_ipyexec_activate)]
self._action_group.add_actions(actions)
manager.insert_action_group(self._action_group, -1)
self._ui_id = manager.add_ui_from_string(ui_str)
# Panel
self.textview = gtk.TextView()
self.textview.show()
self.outputpanel = gtk.ScrolledWindow()
self.outputpanel.set_policy(gtk.POLICY_AUTOMATIC, gtk.POLICY_AUTOMATIC)
self.outputpanel.set_shadow_type(gtk.SHADOW_IN)
self.outputpanel.show()
self.outputpanel.add(self.textview)
bottom = self._window.get_bottom_panel()
bottom.add_item(self.outputpanel, "Output", "Output")
def deactivate(self, window):
manager = self._window.get_ui_manager()
manager.remove_ui(self._ui_id)
manager.remove_action_group(self._action_group)
manager.ensure_update()
# Panel
bottom = self._window.get_bottom_panel()
bottom.remove_item(self.outputpanel)
def update_ui(self, window):
pass
def on_ipyexec_activate(self, action):
# Show Buttom Panel
bottom = self._window.get_bottom_panel()
bottom.show()
# Buffer
buf = self.textview.get_buffer()
# Get full path
view = self._window.get_active_view()
doc = view.get_buffer()
location = doc.get_location()
path = location.get_path()
# Popen
popen = subprocess.Popen(
[IPYPATH, path],
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE )
output = popen.communicate()
if output[1]:
buf.set_text("Do IronPython\n\n%s\nDone." % output[1])
else:
if output[0]:
buf.set_text("Do IronPython\n\n%s\nDone." % output[0])
else:
buf.set_text("Do IronPython\n\nNo Output\n\nDone.")
なんとか動く、かなり手抜きくさいのはご了承。
External Tools と違って終了するまで値が戻ってこない仕様ですんで。
小物ならコレで問題ないけど Application クラスを使うとなると…
即座に stderr を検知したいけど、手段が解らないです。
拡張子判別をしてアプリを振り分ける手もあるけど私的にはコレでいい。
別の言語で起動させたい人はお好みに書き換えてください。
これ以上改造するにしても、GTK2, gconf, Python2, PyGtk…
本体及びプラグインの構成部品がことごとく既に開発終了しているという現実がね。
Gedit3 の Windows パッケージが出るならもう少し本気になるかも。
ということで。
Linux でも Windows でも動くことを考慮しなければプラグインは作れます。
ただ Windows で PyGtk を勉強しても他で何も役に立たない、しかも開発終了品。
なので他人に勧め辛いのが難点、Python の勉強にはなるけど。
もっとイイのを誰かに作ってほしいな(ぉい!
# 2013.11.09 追記
日本語出力ができなかった、日本語 Windows の stdout は cp932 なので変換。
それと output を別スレッドにして動作を判り易く改良してみた。
終了まで出力しないのは変わらないけど。
#-*- coding:utf8 -*-
import gedit
import gtk
import os
import subprocess
import glib
IPYPATH = "C:\Program Files (x86)\IronPython 2.7\ipyw64.exe"
ui_str = """<ui>
<menubar name="MenuBar">
<menu name="ToolsMenu" action="Tools">
<menuitem name="ipyexec" action="ipyexec"/>
</menu>
</menubar>
</ui>
"""
class IpyExecPlugin(gedit.Plugin):
def __init__(self):
gedit.Plugin.__init__(self)
def activate(self, window):
self._window = window
manager = self._window.get_ui_manager()
self._action_group = gtk.ActionGroup("IpyExecActions")
# GtkActionEntry
# name, stock_id, label, accelerator, tooltip, callback
actions = [("ipyexec", None, "ipyexec", "F5", "ipyexec", self.on_ipyexec_activate)]
self._action_group.add_actions(actions)
manager.insert_action_group(self._action_group, -1)
self._ui_id = manager.add_ui_from_string(ui_str)
# Panel
self.textview = gtk.TextView()
self.textview.show()
self.outputpanel = gtk.ScrolledWindow()
self.outputpanel.set_policy(gtk.POLICY_AUTOMATIC, gtk.POLICY_AUTOMATIC)
self.outputpanel.set_shadow_type(gtk.SHADOW_IN)
self.outputpanel.show()
self.outputpanel.add(self.textview)
bottom = self._window.get_bottom_panel()
bottom.add_item(self.outputpanel, "Output", "Output")
def deactivate(self, window):
manager = self._window.get_ui_manager()
manager.remove_ui(self._ui_id)
manager.remove_action_group(self._action_group)
manager.ensure_update()
# Panel
bottom = self._window.get_bottom_panel()
bottom.remove_item(self.outputpanel)
def update_ui(self, window):
pass
def on_ipyexec_activate(self, action):
# Show Buttom Panel
bottom = self._window.get_bottom_panel()
bottom.show()
# Write
buf = self.textview.get_buffer()
buf.set_text("Do IronPython\n\n")
glib.idle_add(self.on_idle)
def on_idle(self):
# Buffer
buf = self.textview.get_buffer()
it = buf.get_end_iter()
# Get full path
view = self._window.get_active_view()
doc = view.get_buffer()
location = doc.get_location()
path = location.get_path()
# Popen
popen = subprocess.Popen(
[IPYPATH, path],
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE )
output = popen.communicate()
if output[1]:
buf.insert(it, "%s\nError." % output[1])
elif output[0]:
#buf.insert(it, "%s\nDone." % output[0])
s = unicode(output[0], encoding='cp932').encode("utf8")
buf.insert(it, "%s\nDone." % s)
else:
buf.insert(it, "Done.")
return False
####################
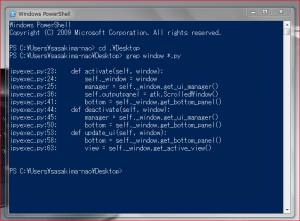
Gedit には grep 機能が無い?
元が Linux のエディタだよ、皆 grep コマンドを使っているからあるわけない。
だから WindowsPowerShell で Select-String コマンドを使いなさい。
つか grep というエイリアスを作ることもできる。
Windows PowerShell の機能
mkdir WindowsPowerShell cd WindowsPowerShell echo Set-Alias grep Select-String > Microsoft.PowerShell_profile.ps1
ドキュメントディレクトリでこんなバッチを動かせば一発よん。
パイプによる stdout も受け付けるし grep コマンドとほぼ同様。
まさか Gedit で grep プラグインを探している偽 Linux 使いはいませんよね。