GtkTable は GTK+3.2 で廃止になっていた。
当面は使えるみたい、だけどいつ無くなるか解らないって怖い。
seemex は GTK+3.0 の時に作ったし公開終了したからからセフセフ。
GtkVBox や GtkHBox という非推奨も使っていたりするがもうシラネ。
しかし GtkGrid を代替で使えということだけど全然引数が違っている。
まず GtkTable は左上が頂点で絶対値にて四角形を指定だった。
GtkGrid は幅と高さを指定、これでは全置換できないので全書き換えになる。
それより attach(…) の引数から Fill や padding を指定することができない。
それらしき関数も見当たらない、ヘルプもチト解りにくい。
どうやらそれらは GtkWidget 側のプロパティで指定するようだ。
こんなプロパティがあったことすら知らなかったが。
GtkWidget.html#GtkWidget–expand
リサイズ時に引き伸ばすなら expand Property を True にする。
padding Property は無いけど margin Property でイケそうだ。
Gtk+ はコンテナ側にこの指定があるのが少し不便だった。
どう考えても子ウイジェット側にあったほうがウイジェットの入れ替えやパレントの変更がスムース、実際 Windows の WPF はそうなっている。
やはり代えたいのだろうと憶測。
GtkBox なんかも今後そうなっていくかもしれない。
reparent した後に set_child_packing 必須って意味わかんなかったし。
さて、これが解ったところで。
いつものように画像検索から面白そうなことをやっていそうな人を探す。
日本人には最初から期待していない、おかげでリンク先が海外ばかりなこのブログ。
しかし今回はイマイチなものしか見当たらない、
教科書的というか、実用的な解説をしている人が見当たらないというか。
しかたがないので自力でやって確認してみる。
seemex の編集部分に使っていた GtkTable を抜いて GtkGrid に書き換えてみた。
非推奨関数とテキトーだったところは書き換え、外国人が解るようにヘタクソな英語で。
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from gi.repository import Gtk
EDITOR_LABELS = ("Name", "Key", "URL", "Query")
EDITOR_CHECK = "Is POST"
ENTER_BUTTON = "_Edit"
class TableWin(Gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
"""
GtkTable has been deprecated. Use GtkGrid instead.
table.attach ( child,
left_attach,
right_attach,
top_attach,
bottom_attach,
xoptions=Gtk.AttachOptions.EXPAND,
yoptions=Gtk.AttachOptions.EXPAND,
xpadding=0,
ypadding=0 )
"""
Gtk.Window.__init__(self)
self.set_title("Table")
self.connect("delete-event", Gtk.main_quit)
# GtkTable
table = Gtk.Table(5, 3)
# Edit Widget
self.edit_name = Gtk.Entry()
table.attach(self.edit_name, 1, 2, 0, 1)
self.edit_key = Gtk.Entry()
table.attach(self.edit_key, 3, 4, 0, 1, Gtk.AttachOptions.FILL)
self.edit_url = Gtk.Entry()
table.attach(self.edit_url, 1, 5, 1, 2)
self.edit_query = Gtk.Entry()
table.attach(self.edit_query, 1, 4, 2, 3)
self.check_post = Gtk.CheckButton.new_with_label(EDITOR_CHECK)
table.attach(self.check_post, 4, 5, 2, 3, Gtk.AttachOptions.FILL)
# Label
labels = []
for label in EDITOR_LABELS:
labels.append(Gtk.Label(label))
table.attach(labels[0], 0, 1, 0, 1, Gtk.AttachOptions.FILL)
table.attach(labels[1], 2, 3, 0, 1, Gtk.AttachOptions.FILL, xpadding=10)
table.attach(labels[2], 0, 1, 1, 2, Gtk.AttachOptions.FILL)
table.attach(labels[3], 0, 1, 2, 3, Gtk.AttachOptions.FILL)
# Button
self.button = Gtk.Button.new_with_mnemonic(ENTER_BUTTON)
table.attach(self.button, 4, 5, 0, 1, Gtk.AttachOptions.FILL)
#
self.add(table)
self.show_all()
TableWin()
Gtk.main()
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from gi.repository import Gtk
EDITOR_LABELS = ("Name", "Key", "URL", "Query")
EDITOR_CHECK = "Is POST"
ENTER_BUTTON = "_Edit"
class GridWin(Gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
"""
GtkGrid
grid.attach(child, left, top, width, height)
or
grid.attach_next_to(child, sibling, GtkPositionType, width, height)
GtkAttachOptions to GtkWidget 'expand' Property
Padding to GtkWidget 'margin' Property
"""
Gtk.Window.__init__(self)
self.set_title("Grid")
self.connect("delete-event", Gtk.main_quit)
# GtkGrid
grid = Gtk.Grid.new()
# Edit Widget
self.edit_name = Gtk.Entry()
# Substitute Gtk.AttachOptions.EXPAND
self.edit_name.props.expand = True
grid.attach(self.edit_name, 1, 0, 1, 1)
self.edit_key = Gtk.Entry()
grid.attach(self.edit_key, 3, 0, 1, 1)
self.edit_url = Gtk.Entry()
self.edit_url.props.expand = True
grid.attach(self.edit_url, 1, 1, 5, 1)
self.edit_query = Gtk.Entry()
self.edit_query.props.expand = True
grid.attach(self.edit_query, 1, 2, 3, 1)
self.check_post = Gtk.CheckButton.new_with_label(EDITOR_CHECK)
grid.attach(self.check_post, 4, 2, 1, 1)
# Label
labels = []
for label in EDITOR_LABELS:
labels.append(Gtk.Label(label))
grid.attach(labels[0], 0, 0, 1, 1)
grid.attach(labels[1], 2, 0, 1, 1)
grid.attach(labels[2], 0, 1, 1, 1)
grid.attach(labels[3], 0, 2, 1, 1)
# Substitute xpadding
labels[1].props.margin_left = 10
labels[1].props.margin_right = 10
# Button
self.button = Gtk.Button.new_with_mnemonic(ENTER_BUTTON)
grid.attach(self.button, 4, 0, 1, 1)
self.add(grid)
self.show_all()
GridWin()
Gtk.main()
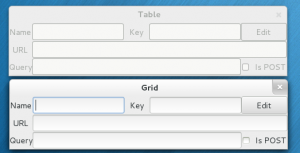
よしリサイズでの引き伸ばされかたも完全に同じだ。
GtkGrid はデフォルトが Fill なので引き伸ばしたい Widget の expand を True にすればいいということなのね。
つか、やっぱりコードは似ているようで全然違うわw
子ウイジェット側で引き延ばし指定を行うほうがやはり理解しやすいなと思う。
たとえ記述量が多くなっても理解しやすいほうがいいなと。