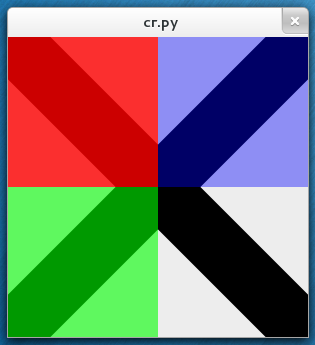
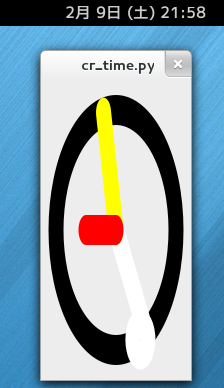
Cairo Tutorial for Python Programmers
のサンプルコードで値が異様に小さい理由が解らなかった。
単純にコピペすると 1px にしか描写しない、なので DrawingArea サイズ得て計算する方法を覚書ページに書いた。
なんてことない、cairo_scale() で cairo のほうをサイズ指定すればよかったのね。
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from gi.repository import Gtk
import cairo
class DrawTest(Gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
Gtk.Window.__init__(self)
da = Gtk.DrawingArea()
da.connect("draw", self.on_draw)
#da.set_double_buffered(False)
self.add(da)
self.connect("delete-event", Gtk.main_quit)
self.resize(300, 300)
self.show_all()
def on_draw(self, widget, cr):
# Get DrawingArea Size
width = widget.get_allocated_width()
height = widget.get_allocated_height()
# cairo Change Size
cr.scale(width, height)
#
cr.set_source_rgb(0, 0, 0)
cr.move_to(0, 0)
cr.line_to(1, 1)
cr.move_to(1, 0)
cr.line_to(0, 1)
cr.set_line_width(0.2)
cr.stroke()
cr.rectangle(0, 0, 0.5, 0.5)
cr.set_source_rgba(1, 0, 0, 0.80)
cr.fill()
cr.rectangle(0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
cr.set_source_rgba(0, 1, 0, 0.60)
cr.fill()
cr.rectangle(0.5, 0, 0.5, 0.5)
cr.set_source_rgba(0, 0, 1, 0.40)
cr.fill()
if __name__ == '__main__':
w = DrawTest()
Gtk.main()
cr.scale(width, height)
だけでサンプルコードがそのまんまコピペできた。
とにかく覚書ページの書き換えか、あーあ。
Boxes 仮想マシンの Lubuntu 上でも問題なく動いた。
しかしこのサンプルは一旦領域を塗りつぶす処理が入っていないのでダブルバッファを無効ににしてリサイズすると悲惨だ。
clutter – A toolkit for creating fast, portable, compelling dynamic UIs
このサンプルを見て気がついた、Clutter での 2D 表示も cairo なのね。
しかし Ubuntu には Clutter がデフォルトで入らないので困る。
海外で GTK+ 等のコードを検索すると皆 Ubuntu ばかり使っていて正直驚く。
ということで PyGI で DrawingArea に表示に作り替えてみた。
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from gi.repository import Gtk, GLib
import cairo, math
class DrawTest(Gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
Gtk.Window.__init__(self)
da = Gtk.DrawingArea()
da.connect("draw", self.on_draw)
self.add(da)
self.connect("delete-event", Gtk.main_quit)
self.resize(150, 300)
self.show_all()
GLib.timeout_add(1000, self.on_timer, da)
def on_timer(self, da):
da.queue_draw()
return True
def on_draw(self, widget, cr):
# get the current time and compute the angles
now = GLib.DateTime.new_now_local()
seconds = GLib.DateTime.get_second(now) * GLib.PI / 30
minutes = GLib.DateTime.get_minute(now) * GLib.PI / 30
hours = GLib.DateTime.get_hour(now) * GLib.PI / 6
# scale the modelview to the size of the surface
width = widget.get_allocated_width()
height = widget.get_allocated_height()
cr.scale(width, height)
cr.set_line_cap(cairo.LINE_CAP_ROUND)
cr.set_line_width(0.1)
# the black rail that holds the seconds indicator
cr.set_source_rgb(0, 0, 0)
cr.translate(0.5, 0.5)
cr.arc(0, 0, 0.4, 0, GLib.PI * 2)
cr.stroke()
# the seconds hand
cr.set_source_rgb(1, 1, 1)
cr.move_to(0, 0)
cr.arc(math.sin(seconds) * 0.4, - math.cos(seconds) * 0.4, 0.05, 0, GLib.PI * 2)
cr.stroke()
# the minutes hand
cr.set_source_rgb(1, 1, 0)
cr.move_to(0, 0)
cr.line_to(math.sin(minutes) * 0.4, - math.cos(minutes) * 0.4)
cr.stroke()
# the hours hand
cr.set_source_rgb(1, 0, 0)
cr.move_to(0, 0)
cr.line_to(math.sin(hours) * 0.2, - math.cos(hours) * 0.2)
cr.stroke()
if __name__ == '__main__':
w = DrawTest()
Gtk.main()
GLib に sinf 関数くらい有りそうなのに見つからなかったので math を利用。
GLib.Math.sinf ? glib-2.0
Vala なら有るんだが、C 言語に sinf 関数があるから不要ということか。
それから色はテキトーです。
うん、基本的に cairo で使う数値は 0.0〜1.0 でいいみたい。
スマートフォンのような拡縮を考えるとそういう方向になるわけで。
作り手としては画面サイズ計算をする必要が無いというのも嬉しいですね。